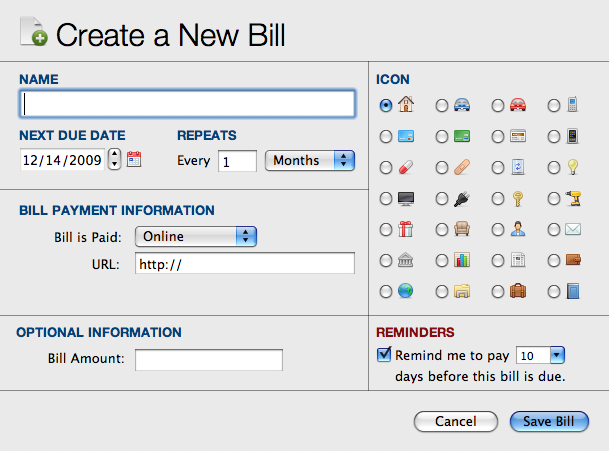
Paying Bill Programs For Mac
Mac Apple. Logic Pro XLogic Pro puts a complete recording and MIDI production studio on your Mac, with everything you need to write, record, edit, and mix like never before. And with a huge collection of full featured plug ins along with thousands of sounds and loops, youll have everything you need to go from first inspiration to final master, no matter what kind of music you want to create. Learn moreabout Logic Pro X. A jumbo is a loan in which the amount borrowed is greater than loan limit set by Fannie May FNMA Freddie Mac FHLMC. If you need help paying your bill, whether or not you have insurance, please contact our financial assistance office. By David Ridpath Post originally appears at theconversation. Xvi32 Hex-Editor Program here. Parents, government officials, and tuitionpaying students are all seeking solutions to. Windows PCs are notoriously junkfilled outofthebox. Buy a Microsoft Signature PC from a Microsoft Store yes, Microsoft has a handful of stores across the US and. Internet running slow I tell you how to speed it up for free. The Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation FHLMC, known as Freddie Mac, is a public governmentsponsored enterprise GSE, headquartered in the Tysons, Virginia. Explore the world of Mac. Check out the MacBook Pro, iMac Pro, MacBook, iMac, and more. Visit the Apple site to learn, buy, and get support. Amazon wants to reward you for buying stuff from them, but theres a catch you have to use your debit card and transfer cash into an Amazon account. Its not. 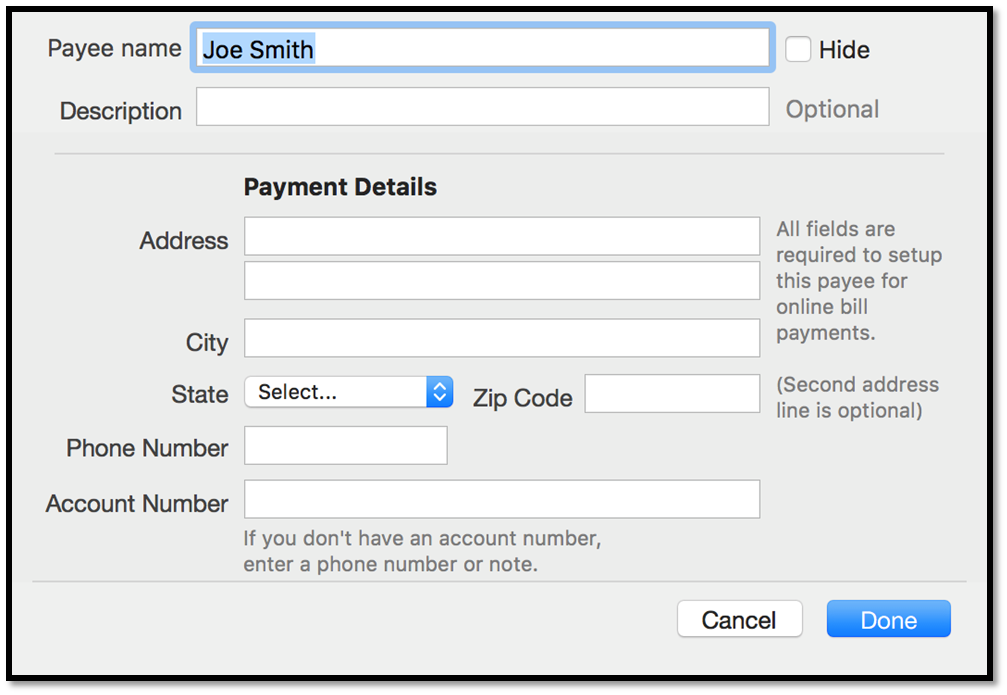

 Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2. The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2. Division A of Pub. L. 1. 103. 43, 1. Stat. 3. 76. 5, enacted October 3, 2. U. S. financial system, is a law enacted in response to the subprime mortgage crisis authorizing the United States Secretary of the Treasury to spend up to 7. The funds for purchase of distressed assets were mostly redirected to inject capital into banks and other financial institutions while the Treasury continued to examine the usefulness of targeted asset purchases. Both foreign and domestic banks are included in the program. The Act was proposed by Treasury Secretary. Henry Paulson during the global financial crisis of 2. President. George W. Bush on October 3, 2. HistoryeditThe legislation had its origin in early 2. Secretary of the Treasury. Henry Paulson directed two of his aides, Neel Kashkari and Phillip Swagel, to write a plan to recapitalize the U. S. financial system in case of total collapse. The plan, which was also presented to Federal Reserve Chairman. Ben Bernanke, called for the U. S. government to purchase about 5. The original proposal was submitted to the United States House of Representatives, with the purpose of purchasing bad assets, reducing uncertainty regarding the worth of the remaining assets, and restoring confidence in the credit markets. The bill was then expanded and put forth as an amendment to H. R. 3. 99. 7. 4 The amendment was rejected via a vote of the House of Representatives on September 2. Supporters of the plan argued that the market intervention called for by the plan was vital to prevent further erosion of confidence in the U. S. credit markets and that failure to act could lead to an economic depression. Opponents objected to the plans cost and rapidity, pointing to polls that showed little support among the public for bailing out Wall Street investment banks,6 claimed that better alternatives were not considered,7 and that the Senate forced passage of the unpopular version through the opposing house by sweetening the bailout package. On October 1, 2. Senate debated and voted on an amendment to H. R. 1. 42. 4, which substituted a newly revised version of the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2. H. R. 1. 42. 4. 91. The Senate accepted the amendment and passed the entire amended bill, voting 7. Additional unrelated provisions added an estimated 1. See. Public Law 1. The amended version of H. R. 1. 42. 4 was sent to the House for consideration, and on October 3, the House voted 2. President George W. Bush signed the bill into law within hours of its congressional enactment, creating the 7. Troubled Asset Relief Program TARP to purchase failing bank assets. On October 8, the British announced their bank rescue package consisting of funding, debt guarantees and infusing capital into banks via preferred stock. This model was closely followed by the rest of Europe, as well as the U. S Government, who on the October 1. Capital Purchase Program to buy stakes in a wide variety of banks in an effort to restore confidence in the sector. The money came from the 7. Troubled Asset Relief Program. Over the next six months, TARP was dwarfed by other guarantees and lending limits analysis by Bloomberg found the Federal Reserve had, by March 2. U. S. that year. 1. Economic backgroundeditAfter the freeing up of world capital markets in the 1. GlassSteagall Act in 1. Greenspan inspired self regulation along with monetized subprime mortgages sold as no risk investments, reached a critical stage during September 2. In response, the U. S. government announced a series of comprehensive steps to address the problems, following a series of one off or case by case decisions to intervene or not, such as the 8. American International Group on September 1. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, and the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers. On Monday, October 6, the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped more than 7. The same day, CNN reported these worldwide stock market events 2. Britains FTSE 1. Index was down 7. Germanys DAX down 7. Frances CAC 4. 0 dropping 9In Russia, trading in shares was suspended after the RTS stock index fell more than 2. Iceland halted trading in six bank stocks while the government drafted a crisis plan. Paulson proposaleditU. S. Treasury Secretary. Henry Paulson proposed a plan under which the U. S. Treasury would acquire up to 7. The plan was immediately backed by President George W. Bush and negotiations began with leaders in the U. S. Congress to draft appropriate legislation. President Bush meets with Congressional members, including presidential candidates John Mc. Cain and Barack Obama, at the White House to discuss the bailout, September 2. Consultations among Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson, Chairman of the Federal Reserve. Ben Bernanke, U. S. Securities and Exchange Commission chairman Christopher Cox, congressional leaders, and President Bush, moved forward efforts to draft a proposal for a comprehensive solution to the problems created by illiquid assets. News of the coming plan resulted in some stock, bond, and currency markets stability on September 1. The proposal called for the federal government to buy up to US7. The draft proposal was received favorably by investors in the stock market, but caused the U. S. dollar to fall against gold, the Euro, and petroleum. The plan was not immediately approved by Congress debate and amendments were seen as likely before the plan was to receive legislative enactment. Throughout the week of September 2. Congress over the terms and scope of the bailout,3. Washington Mutual, and the upcoming November 4 national election. On September 2. 1, Paulson announced that the original proposal, which would have excluded foreign banks, had been revised to include foreign financial institutions with a presence in the United States. The U. S. administration pressured other countries to set up similar bailout plans. On September 2. 3, the plan was presented by Paulson and Bernanke to the Senate Banking Committee, who rejected it as unacceptable. On September 2. 4, President Bush addressed the nation on prime time television, describing how serious the financial crisis could become if action was not taken promptly by Congress. Also on September 2. Republican Party nominee for President, John Mc. Cain, and Democratic Party nominee for President, Barack Obama, issued a joint statement describing their shared view that The effort to protect the American economy must not fail. The plan was introduced on September 2. Paulson. Named the Troubled Asset Relief Program,2. Paulson Proposal or Paulson Plan, it should not be confused with Paulsons earlier 2. Blueprint for a Modernized Financial Regulatory Reform,3. March 3. 1, 2. 00. The proposal was only three pages long, intentionally short on details to facilitate quick passage by Congress. Convert Jpg To Autocad Dxf. Mortgage asset purchaseseditA key part of the proposal is the federal governments plan to buy up to 7. MBS with the intent to increase the liquidity of the secondary mortgage markets and reduce potential losses encountered by financial institutions owning the securities. The draft proposal of the plan was received favorably by investors in the stock market. This plan can be described as a risky investment, as opposed to an expense. The MBS within the scope of the purchase program have rights to the cash flows from the underlying mortgages.
Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2. The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2. Division A of Pub. L. 1. 103. 43, 1. Stat. 3. 76. 5, enacted October 3, 2. U. S. financial system, is a law enacted in response to the subprime mortgage crisis authorizing the United States Secretary of the Treasury to spend up to 7. The funds for purchase of distressed assets were mostly redirected to inject capital into banks and other financial institutions while the Treasury continued to examine the usefulness of targeted asset purchases. Both foreign and domestic banks are included in the program. The Act was proposed by Treasury Secretary. Henry Paulson during the global financial crisis of 2. President. George W. Bush on October 3, 2. HistoryeditThe legislation had its origin in early 2. Secretary of the Treasury. Henry Paulson directed two of his aides, Neel Kashkari and Phillip Swagel, to write a plan to recapitalize the U. S. financial system in case of total collapse. The plan, which was also presented to Federal Reserve Chairman. Ben Bernanke, called for the U. S. government to purchase about 5. The original proposal was submitted to the United States House of Representatives, with the purpose of purchasing bad assets, reducing uncertainty regarding the worth of the remaining assets, and restoring confidence in the credit markets. The bill was then expanded and put forth as an amendment to H. R. 3. 99. 7. 4 The amendment was rejected via a vote of the House of Representatives on September 2. Supporters of the plan argued that the market intervention called for by the plan was vital to prevent further erosion of confidence in the U. S. credit markets and that failure to act could lead to an economic depression. Opponents objected to the plans cost and rapidity, pointing to polls that showed little support among the public for bailing out Wall Street investment banks,6 claimed that better alternatives were not considered,7 and that the Senate forced passage of the unpopular version through the opposing house by sweetening the bailout package. On October 1, 2. Senate debated and voted on an amendment to H. R. 1. 42. 4, which substituted a newly revised version of the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2. H. R. 1. 42. 4. 91. The Senate accepted the amendment and passed the entire amended bill, voting 7. Additional unrelated provisions added an estimated 1. See. Public Law 1. The amended version of H. R. 1. 42. 4 was sent to the House for consideration, and on October 3, the House voted 2. President George W. Bush signed the bill into law within hours of its congressional enactment, creating the 7. Troubled Asset Relief Program TARP to purchase failing bank assets. On October 8, the British announced their bank rescue package consisting of funding, debt guarantees and infusing capital into banks via preferred stock. This model was closely followed by the rest of Europe, as well as the U. S Government, who on the October 1. Capital Purchase Program to buy stakes in a wide variety of banks in an effort to restore confidence in the sector. The money came from the 7. Troubled Asset Relief Program. Over the next six months, TARP was dwarfed by other guarantees and lending limits analysis by Bloomberg found the Federal Reserve had, by March 2. U. S. that year. 1. Economic backgroundeditAfter the freeing up of world capital markets in the 1. GlassSteagall Act in 1. Greenspan inspired self regulation along with monetized subprime mortgages sold as no risk investments, reached a critical stage during September 2. In response, the U. S. government announced a series of comprehensive steps to address the problems, following a series of one off or case by case decisions to intervene or not, such as the 8. American International Group on September 1. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, and the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers. On Monday, October 6, the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped more than 7. The same day, CNN reported these worldwide stock market events 2. Britains FTSE 1. Index was down 7. Germanys DAX down 7. Frances CAC 4. 0 dropping 9In Russia, trading in shares was suspended after the RTS stock index fell more than 2. Iceland halted trading in six bank stocks while the government drafted a crisis plan. Paulson proposaleditU. S. Treasury Secretary. Henry Paulson proposed a plan under which the U. S. Treasury would acquire up to 7. The plan was immediately backed by President George W. Bush and negotiations began with leaders in the U. S. Congress to draft appropriate legislation. President Bush meets with Congressional members, including presidential candidates John Mc. Cain and Barack Obama, at the White House to discuss the bailout, September 2. Consultations among Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson, Chairman of the Federal Reserve. Ben Bernanke, U. S. Securities and Exchange Commission chairman Christopher Cox, congressional leaders, and President Bush, moved forward efforts to draft a proposal for a comprehensive solution to the problems created by illiquid assets. News of the coming plan resulted in some stock, bond, and currency markets stability on September 1. The proposal called for the federal government to buy up to US7. The draft proposal was received favorably by investors in the stock market, but caused the U. S. dollar to fall against gold, the Euro, and petroleum. The plan was not immediately approved by Congress debate and amendments were seen as likely before the plan was to receive legislative enactment. Throughout the week of September 2. Congress over the terms and scope of the bailout,3. Washington Mutual, and the upcoming November 4 national election. On September 2. 1, Paulson announced that the original proposal, which would have excluded foreign banks, had been revised to include foreign financial institutions with a presence in the United States. The U. S. administration pressured other countries to set up similar bailout plans. On September 2. 3, the plan was presented by Paulson and Bernanke to the Senate Banking Committee, who rejected it as unacceptable. On September 2. 4, President Bush addressed the nation on prime time television, describing how serious the financial crisis could become if action was not taken promptly by Congress. Also on September 2. Republican Party nominee for President, John Mc. Cain, and Democratic Party nominee for President, Barack Obama, issued a joint statement describing their shared view that The effort to protect the American economy must not fail. The plan was introduced on September 2. Paulson. Named the Troubled Asset Relief Program,2. Paulson Proposal or Paulson Plan, it should not be confused with Paulsons earlier 2. Blueprint for a Modernized Financial Regulatory Reform,3. March 3. 1, 2. 00. The proposal was only three pages long, intentionally short on details to facilitate quick passage by Congress. Convert Jpg To Autocad Dxf. Mortgage asset purchaseseditA key part of the proposal is the federal governments plan to buy up to 7. MBS with the intent to increase the liquidity of the secondary mortgage markets and reduce potential losses encountered by financial institutions owning the securities. The draft proposal of the plan was received favorably by investors in the stock market. This plan can be described as a risky investment, as opposed to an expense. The MBS within the scope of the purchase program have rights to the cash flows from the underlying mortgages.